
35 CSS Selectors to remember
CSS Selectors help to select HTML elements (ex: DIV, P, H1) to apply styles.
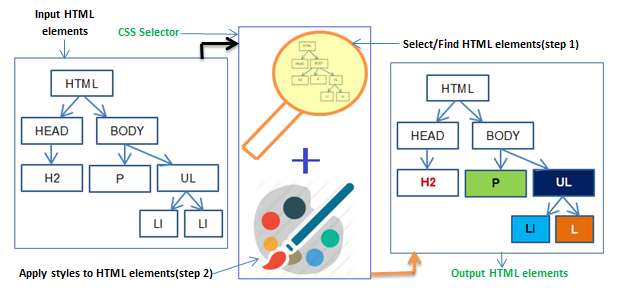
CSS selector does the following works.
- Selects the HTML element(s).
- Apply specified CSS styles.
Why we need CSS selectors?
Every HTML page is a collection of HTML elements. Internally all HTML elements are linked using DOM. Different CSS selectors are used to find/select HTML elements from the DOM tree to style.
1. Universal Selector (*)
“*” denotes universal selector. Universal selector is used to select every HTML element to apply styles.
div *{
color:red;
}
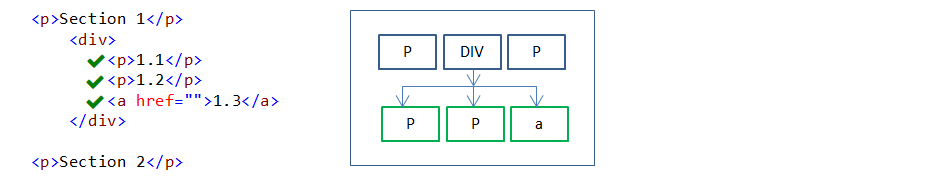
In the above example, every child element under the DIV element is styled.
Universal selector vs Body selector:
Universal selector:
- It selects and applies styles to all elements.
- It overrides default inherited properties of the elements.
- Since it selects all the elements, its weight is more.
Body selector:
- It selects and applies style only to BODY element.
- Many child elements(not all) inherit BODY element properties and applies.
2. Class Selectors
Class selector is used to select CSS class applied HTML elements to apply styles. Class selector starts with ‘.” followed by name(ex: .section). This is one of the mostly used selector.
.section{
color:red;
position:relative;
left:50px;
}
.section-heading {
font-weight:bold;
}
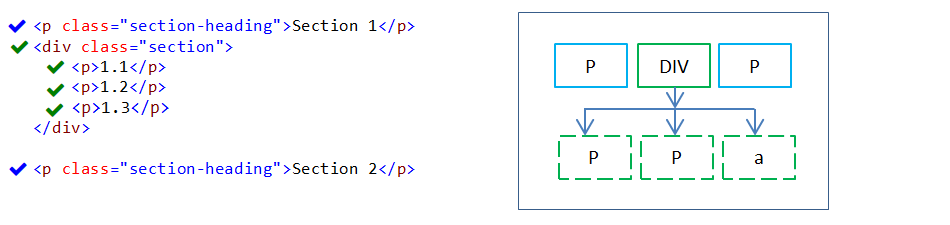
In the above example,
- Two different class selectors(“.section”, “section-heading”) are applied to HTML elements.
- “section-heading” class applied P elements(2) are styled.
- “section” class is applied to DIV element. It has three properties. Following are results.
- Left style property is applied to the DIV element. Its child(three P) elements didn’t inherit “left” style property.
- Color style property is applied to the DIV element. Its child(three P) elements inherited color style property from the parent DIV element.
3. ID Selectors
ID selector is used to select specified ID applied HTML element. ID selector starts with ‘#” followed by name(ex: #section1). ID to be unique to an HTML page.
#section-heading1 {
color: red;
}
#section-heading2 {
color: green;
}

In the above example, P elements are styled based on ID.
Note: CSS still works when it finds duplicate ID(more than one element use same ID) in a page. But JavaScript wouldn’t work properly when it access duplicate ID directly in a page.
4. Element Selectors
Element selector is used to select HTML elements based on element type(ex: p, div).
p {
color:red;
}
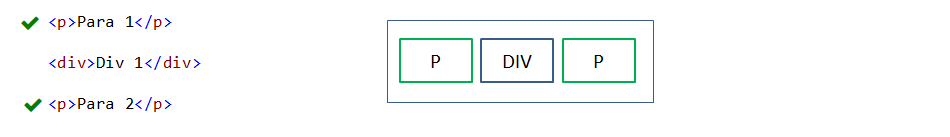
In the above example, text color set to all P elements.
Note: If more than one CSS style declarations apply to the same element then browser decides which specific CSS style declaration to be applied to the element based on some predefined rules. This is called Specificity.
5. Descendant Selectors (S1 S2)
Descendant selector is used to select specified descendant elements under the parent element.
In Descendant selector syntax has two part. First part specifies parent level element and second part specifies descendant level elements.
#section1 p {
color:red;
}
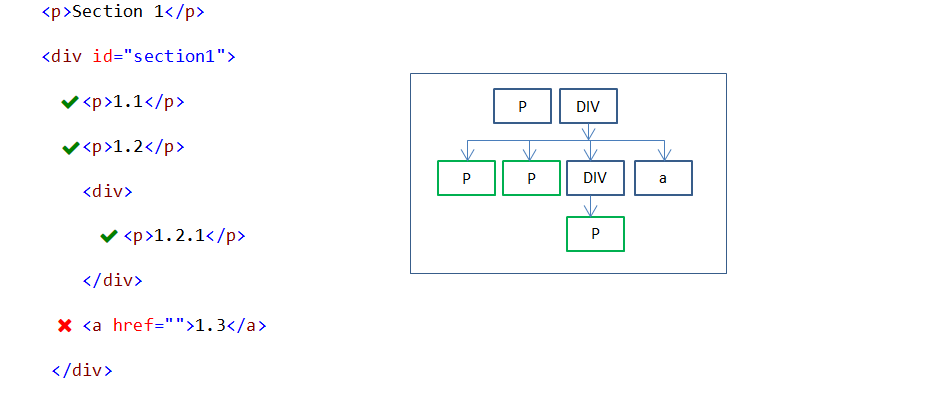
In the above example, all P(descendant) elements under the DIV(parent) element are styled.
Note: Descendant elements includes all level(child, grandchild etc.,) child elements.
Descendant vs Child selectors:
- Descendant selector selects all level(child, grandchild etc.,) child elements but child selector selects only immediate child elements.
6. Child Selectors (S1 > S2)
Child selector is used to select specified direct child elements under the parent element.
Child selectors syntax has two parts. First part specifies parent element and second part specifies child elements.
#section1 > p {
color:red;
}
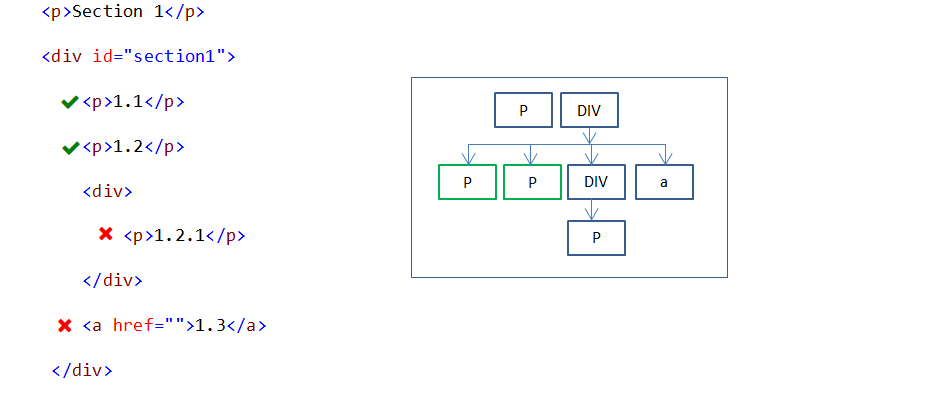
In the above example, all immediate P child elements under the parent element(div id=’#section1’) are styled. Grandchild P element is not styled.
7. Adjacent Sibling Selectors (S1 + S2)
Adjacent sibling selector is used to select a specified element which is immediate next to another specified element. Both elements should be in the same level.
Adjacent sibling selector syntax has two parts(S1 + S2). Second part element(E2) is a target element to select which is immediate next to first part element(S1). Both specified elements are in the same level.
div + p {
color:red;
}
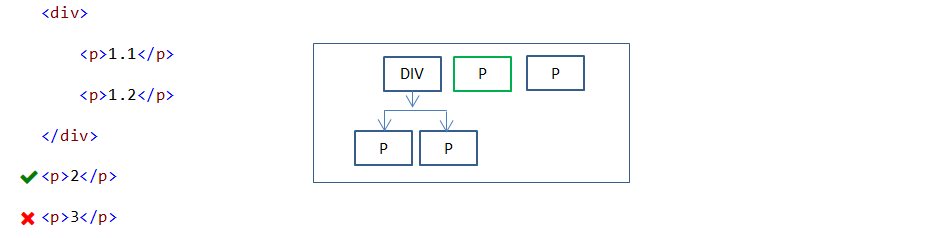
In the above example, first P element after DIV element is only styled.
8. General Sibling Selectors (S1 ~ S2)
General sibling selector is used to select all specified sibling elements of another specified element.
General sibling selector syntax has two parts(S1 ~ S2). Second part elements(S2) are target elements to select which are available after first part element(S1). Both specified elements should be in the same level.
div ~ p {
color:red;
}
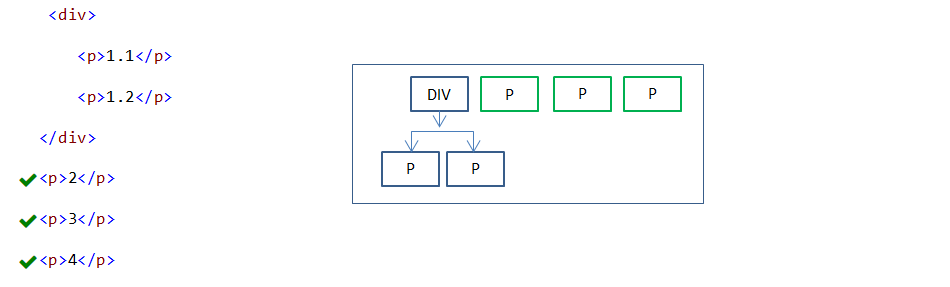
In the above example, all P elements after DIV element are styled.
Adjacent Sibling(S1 + S2) vs General Sibling(S1 ~ S2) selectors:
- Adjacent sibling(S1 + S2) selector selects immediate sibling element only but general sibling(S1 ~ S2) selector selects all sibling elements of another specified element. Both cases, both elements(S1 and S2) should be in the same level.
9. Attribute Selectors ([attribute])
This attribute selector([attribute]) is used to select elements with specified attribute.
div[data-section] {
border:1px solid green;
}
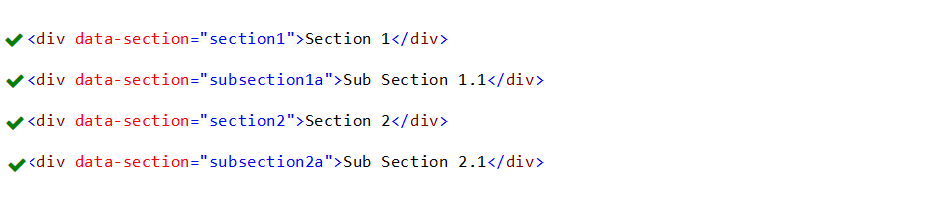
In the above example, DIV elements with attribute “data-section” are styled.
ii) Following code shows to style all elements based on attribute only
[data-section] {
border:1px solid green;
}

In the above example, all elements with attribute([data-section]) are styled.
10. Attribute Selectors ([attribute = value])
This attribute selector([attribute = value]) is used to select elements with specified attribute and value.
div[data-section="section2"] {
border:1px solid green;
}
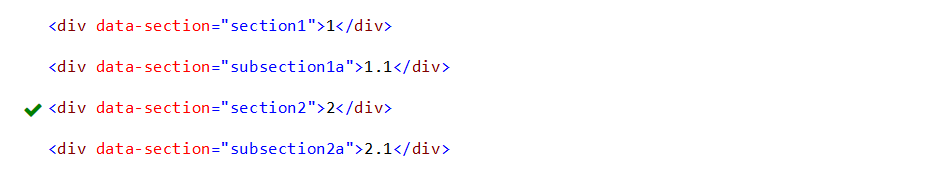
In the above example, DIV element is styled based on attribute(“data-section”) and attribute value(="section2").
11. Attribute Selectors ([attribute ~= value])
This attribute selector([attribute ~= value]) is used to select elements with specified attribute and attribute value contains specified word. Value can have one word or whitespace separated list of words.
[data-value ~="result"] {
border:1px solid green;
}

In the above example, elements with attribute(“data-value”) and attribute value contain word “result” are styled.
12. Attribute Selectors ([attribute |= value])
This attribute selector(attribute |= value) is used to select elements with specified attribute and attribute value exactly equal to a specified value or value starts with specified value immediately followed by a “-“ (hyphen).
[data-value |="result"] {
border:1px solid green;
}
[lang |= "fr"] {
color:red;
}

In the above example,
- Using “data-value” attribute and its value, first element is styled.
- Using “lang” attribute and its value, fourth element is styled. Here attribute value starts with “fr” immediately followed by a “-“ (hyphen).
13. Attribute Selectors ([attribute ^= value])
This attribute selector([attribute ^= value]) is used to select elements with specified attribute and attribute value starts with specified value.
[href ^="https"] {
font-size:1.5em;
}

In the above example, elements with attribute(“href”) and attribute value starts with “https” are styled.
14. Attribute Selectors ([attribute $= value])
This attribute selector([attribute $= value]) is used to select elements with specified attribute and attribute value ends with specified value.
[href $=".com"] {
font-size:1.5em;
}

In the above example, element with attribute “href” and attribute value ends with “.com” is selected.
15. Attribute Selectors ([attribute *= value])
This attribute selector([attribute *= value]) is used to select elements with specified attribute and attribute value should contain specified value.
[href *=".com"] {
font-size:1.5em;
}

In the above example, elements with attribute “href” and attribute value contain “.com” are styled.
Note:
- For [attribute ^= value], attribute value should starts with specified value.
- For [attribute $= value], attribute value should ends with specified value.
- For [attribute *= value], attribute value should contains specified value (at the beginning/end/middle/etc.,).
16. :first-child pseudo-class
:first-child pseudo-class selector is used to select a specified first child element under the parent element.
Note: Pseudo-class selectors have the following syntax.
selector:pseudo-class{ property:value; }
- 1st part specifies selector name(P,#id1, .class1).
- 2nd part is “:” symbol.
- 3rd part specifies pseudo-class name.
- Remaining part specifies style declarations.
p:first-child {
border:1px solid red;
}
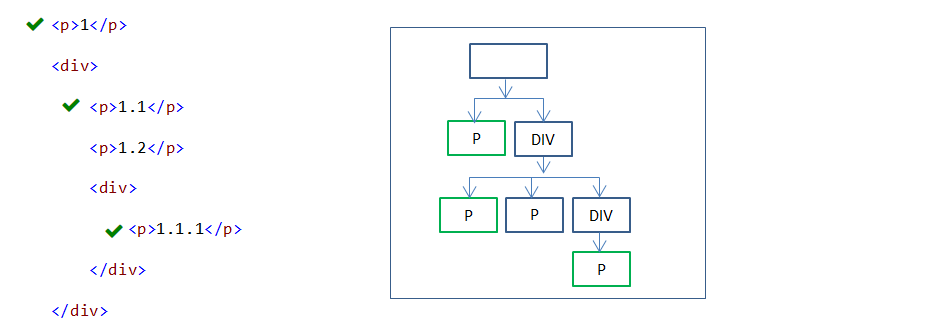
In the above example,
- Three P first child elements are styled.
- First P child element’s parent element is BODY element.
17. :last-child pseudo-class
:last-child pseudo-class selector is used to select a specified last child element under the parent element.
p:last-child {
border:1px solid red;
}
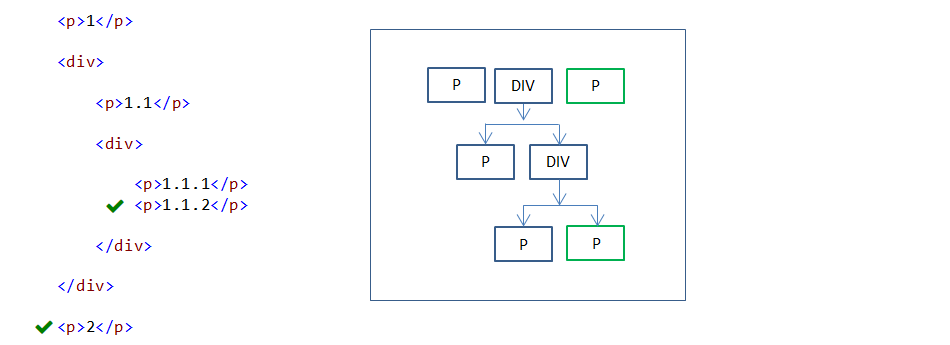
In the above example, last child P elements under the parent element are styled.
18. :only-child pseudo-class
:only-child pseudo-class selector is used to select a specified element when it is the only child element(child element count should be one and that child element should be a specified element) under the parent element.
p:only-child {
border:1px solid red;
}
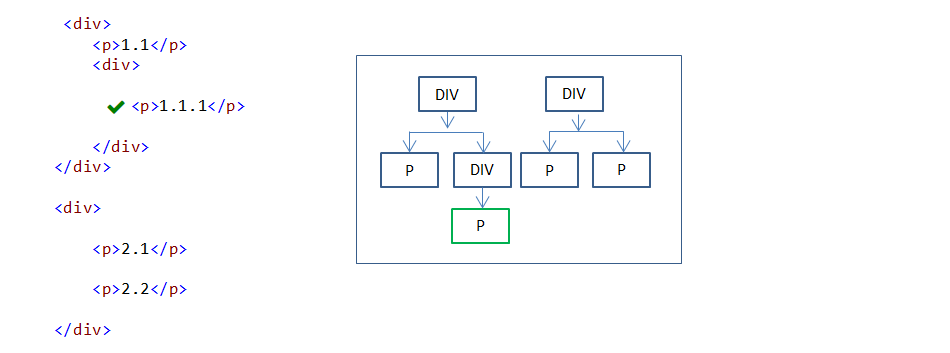
In the above example, P element is the only child element of the one DIV element and it is styled.
19. :only-of-type pseudo-class
:only-of-type pseudo-class selector is used to select a specified element when it is the only child of its type(child element count should be one based on specified element type) under the parent element.
p:only-of-type{
border:1px solid red;
}
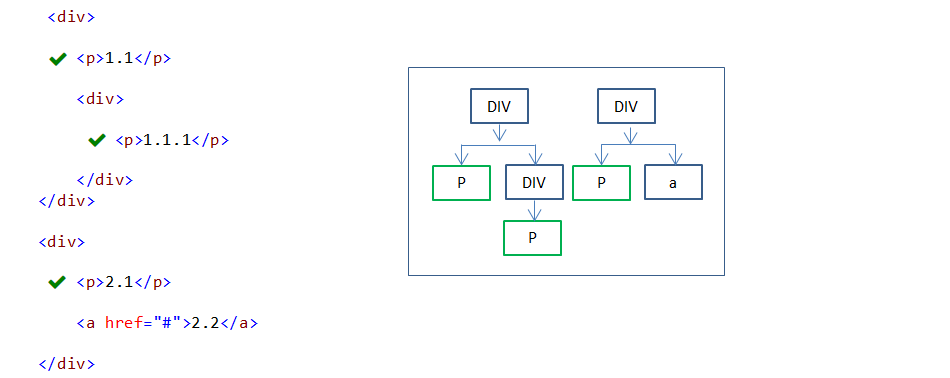
In the above example, three P elements are styled. Each styled P element is the only child element of its type under each parent.
20. :first-of-type pseudo-class
:first-of-type pseudo-class selector is used to select a specified first element of its type under the parent element.
p:first-of-type{
border:1px solid red;
}
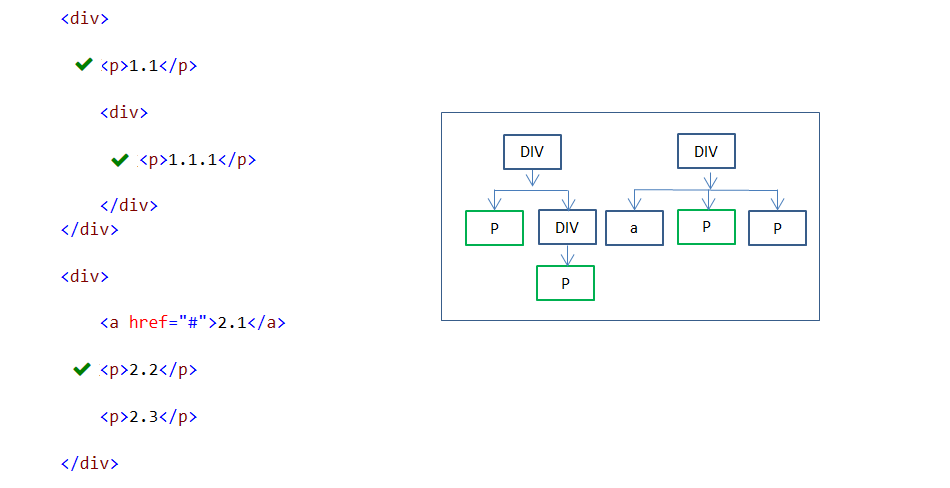
In the above example, three P elements are styled. Each styled P element is the first element of specified type under the parent element.
Note: :first-child,:last-child,:only-child,:only-of-type,:first-of-type pseudo class selectors select only zero/one element under each parent. But pseudo class selectors name start with nth-xxx select zero/one/more elements under each parent.
21. :nth-child(n) pseudo-class
:nth-child(n) pseudo class selector is used to select specified every nth child element under the parent element.
- n can be a number (ex: 2). When n is a number, it selects zero/one elements.
- n can be a keyword(ex: odd/event). When n is a number, it selects zero/one/more elements.
- n can be a formula(ex: 3n+2). When n is a formula, it selects zero/one/more elements. By default, n value starts from 0.
p:nth-child(2n+1){
border:1px solid red;
}
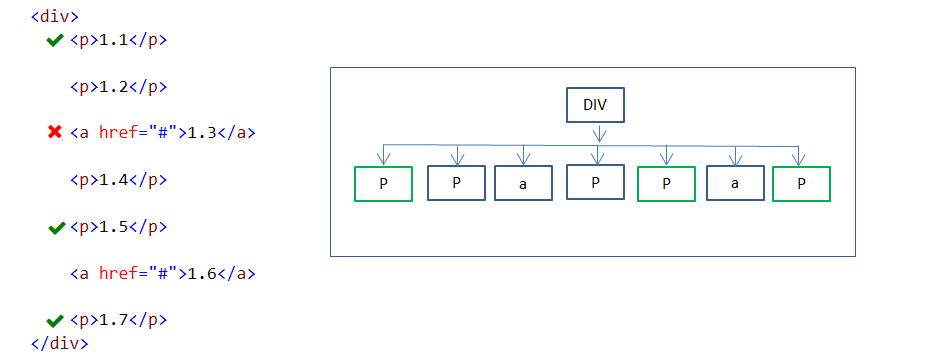
In the above example, 2n+1 formula values are 2*0+1=1, 2*1+1 = 3, 2*2+1 = 5, 2*3+1=7. But 3rd element is not a P element. So 1st, 5th and 7th P elements are styled.
22. :nth-last-child(n) pseudo-class
:nth-last-child(n) pseudo class selector is used to select specified every nth child element(selection order starts from bottom to top) under the parent element.
- n can be a number (ex: 2). When n is a number, it selects zero/one elements.
- n can be a keyword(ex: odd/event). When n is a number, it selects zero/one/more elements.
- n can be a formula(ex: 3n+2). When n is a formula, it selects zero/one/more elements. By default, n value starts from 0.
p:nth-last-child(even){
border:1px solid red;
}
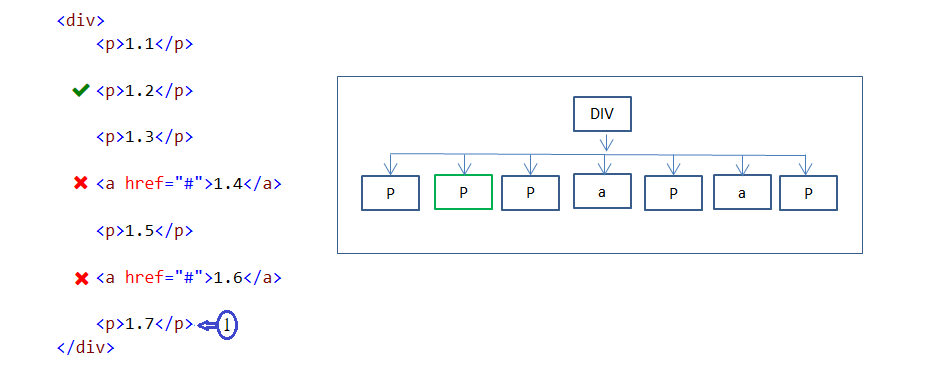
In the above example, applicable even numbers are 2,4 and 6. But 2nd and 4th elements (selection order starts from bottom to top) are not P elements and those are not styled. 6th element is a P element and it is styled.
23. :nth-of-type(n) pseudo-class
:nth-of-type(n) pseudo class selector is used to select specified every nth child element of its type under the parent element.
- n can be a number (ex: 2). When n is a number, it selects zero/one elements.
- n can be a keyword(ex: odd/event). When n is a number, it selects zero/one/more elements.
- n can be a formula(ex: 3n+2). When n is a formula, it selects zero/one/more elements. By default, n value starts from 0.
p:nth-of-type(2n+1){
border:1px solid red;
}
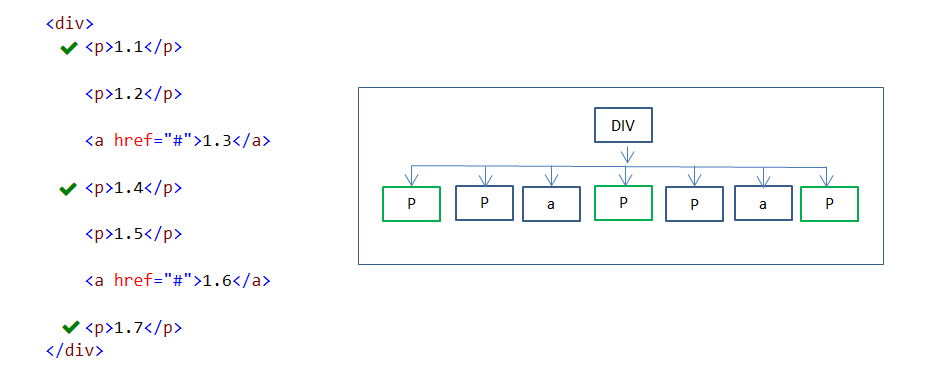
In the above example, 2n+1 formula values are 2*0+1=1, 2*1+1 = 3, 2*2+1 = 5. Here above order only applicable to P elements. So 1st, 3rd and 5th P elements are styled based on its type.
24. :nth-last-of-type(n) pseudo-class
:nth-last-of-type(n) pseudo class selector is used to select specified every nth child element of its type(selection order starts from bottom to top) under the parent element.
- n can be a number (ex: 2). When n is a number, it selects zero/one elements.
- n can be a keyword(ex: odd/event). When n is a number, it selects zero/one/more elements.
- n can be a formula(ex: 3n+2). When n is a formula, it selects zero/one/more elements. By default, n value starts from 0.
p:nth-last-of-type(2n+1){
border:1px solid red;
}
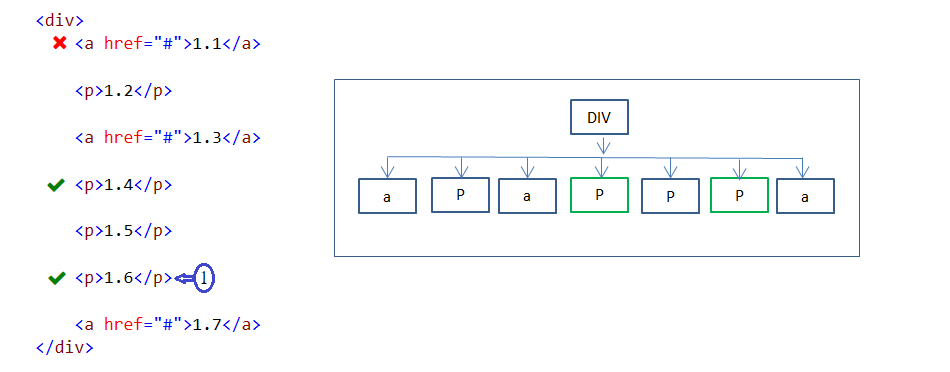
In the above example, 2n+1 formula values are 2*0+1=1, 2*1+1 = 3, 2*2+1 = 5. Here above order only applicable to P elements from bottom to top. So 1sth and 3rd P elements(selection order starts from bottom to top) are styled.
25. :not(selector) pseudo-class
:not(selector) negation pseudo-class selector is used to select specified elements except parameter argument.
p:not(#key-val) {
color:#ff0000;
}
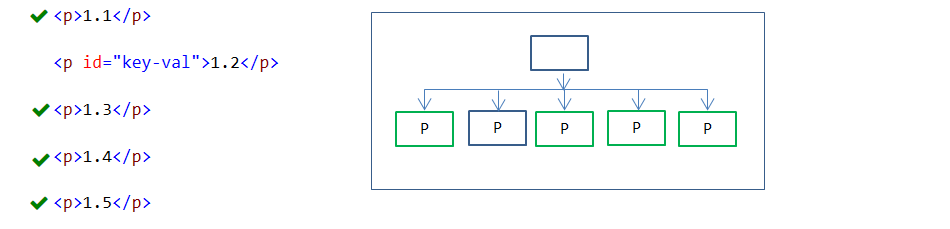
In the above example, all P elements except element with ID = “key-val” are styled.
26. :link pseudo-class
:link pseudo-class is used to select unvisited links.
a:link {
color:green;
}

In the above example, unvisited <a> elements are styled (when page first loads).
27. :visited pseudo-class
:visited pseudo-class is used to select visited links.
a:visited {
color:red;
}

In the above example, visited two <a> elements are styled.
28. :active pseudo-class
:active pseudo-class is used to select currently active element.
p:active, a:active{
font-size:22px;
color:#4cff00;
}- :active pseudo-class applies to focusable and non-focusable elements.
- Multiple selectors separated by comma(ex: p:active, a:active) can help to have same style to different selectors.
29. :focus pseudo-class
:focus pseudo-class is used to select currently focused element.
:focus {
color:#ff0000;
font-size:22px;
}Note: :focus pseudo-class applies to focusable elements only.
30. :hover pseudo-class
:hover pseudo-class is used to select an element when point device over on it.
p:hover {
color:#ff0000;
text-decoration:underline;
}Note: :hover pseudo-class applies to focusable and non-focusable elements.
:active vs :focus
- For focusable elements(ex: hyperlink, textbox, checkbox),
- When element get focus through tab click, :focus pseudo-class applies.
-
When mouse click happens
- Before mouse click release, :active pseudo-class applies.
- After mouse click release, :focus pseudo-class applies.
- In this case, both pseudo-class applies.
- For non-focusable elements(ex: div, p, span),
- When mouse click happens(before mouse click release), :active pseudo-class applies.
- :focus pseudo-class doesn’t apply at any point.
:focus vs :hover
- :focus pseudo-class applies when element gets focus through tab click.
- :focus pseudo-class only applies to focusable elements.
- :hover pseudo-class applies when pointing device over on element.
- :hover pseudo-class applies focusable and non-focusable elements.
31. :root pseudo-class
:root pseudo-class selector is used to select root element. Root element refers HTML element.
:root {
background-color:lightgreen;
margin:25px;
}

In the above example,
- Background-color and margin properties are applied to root(HTML) element only.
- HTML element background color property is inherited by three P elements.
- Margin property is not inherited by any child elements(all 4).
- HTML element background color property is not inherited by text element.
- Property inherited flow is HTML => Body => Child elements.
Note: Child elements inherit parent element’s many(not all) properties.
32. ::before pseudo-elements
::before pseudo-element is used to insert content at the beginning of the specified element content. Inserted content will not be available in the DOM.
div:before{
content:"Section ";
color:#ff0000;
}

In the above example, content(“section”) is added before every DIV element.
Pseudo-elements vs Pseudo-class:
- Pseudo-elements selectors select part of the HTML elements to apply CSS style. But pseudo-class selectors select entire element to apply CSS style.
- Syntax wise, CSS3 pseudo-elements selectors start with “::”(double colons) and pseudo-class selectors start with “:”(single colon).
33. ::after pseudo-elements
::after pseudo-element is used to insert content at the end of the specified element content. Inserted content will not be available in the DOM.
p:after{
content:url("tasks-ok.png");
}

In the above example, content(an image) is added after every P element.
34. ::first-line pseudo-elements
::first-line pseudo-element is used to select first line of the block level(ex: P, DIV) element. This pseudo-element is not applicable on inline(ex: SPAN, EM) elements.
p:first-line{
color:#ff6a00;
font-size:15px;
}

In the above example, first line of the P element is styled. P element is a block level element.
35. ::first-letter pseudo-elements
::first-letter pseudo-element is used to select first letter of the block level(ex: P, DIV) element. This pseudo-element is not applicable on inline(ex: SPAN, EM) elements.
p:first-letter {
font-size:50px;
}
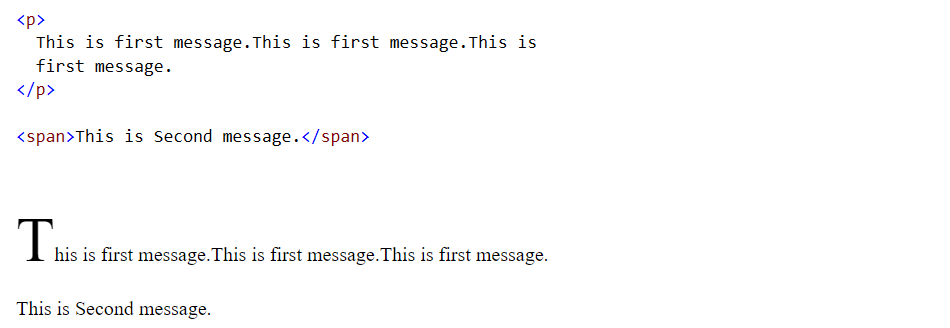
In the above example, first letter of the P(block level) element is styled. SPAN(inline) element is not styled.
CSS Selectors cheat sheet
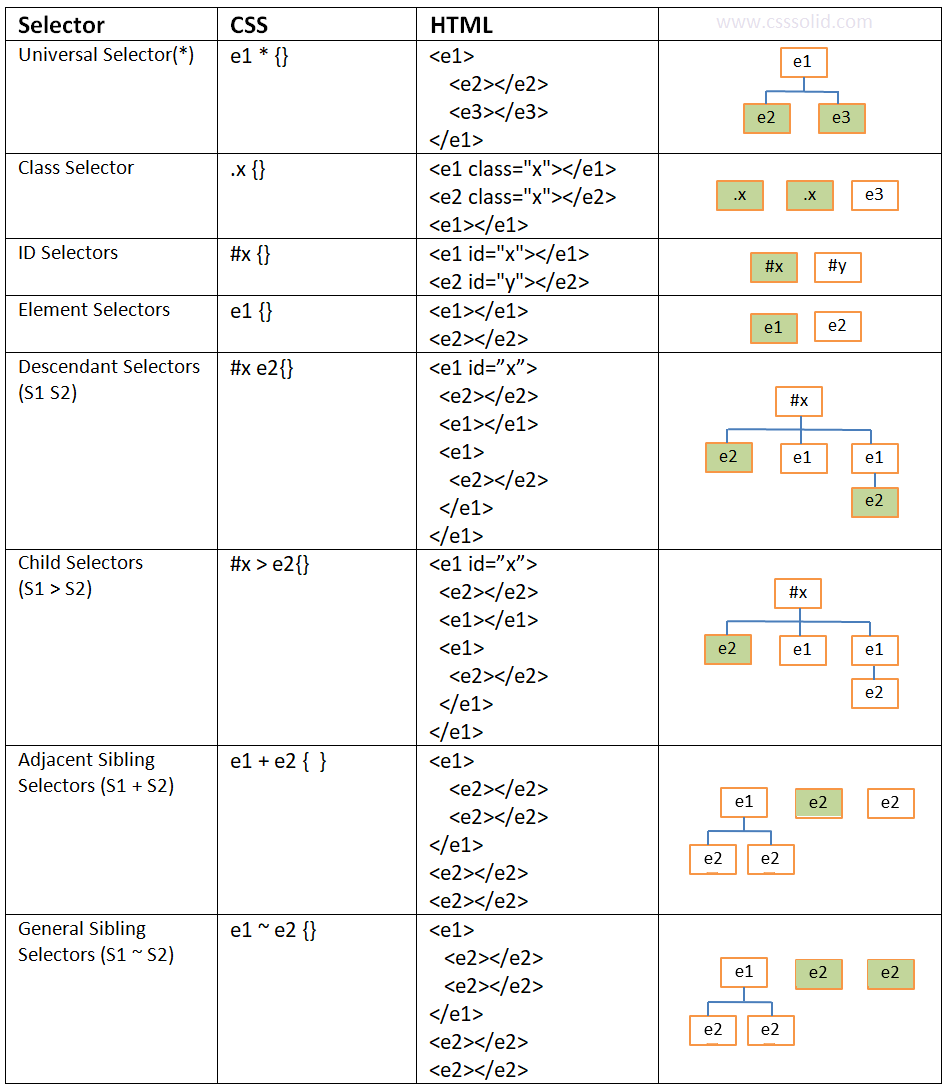
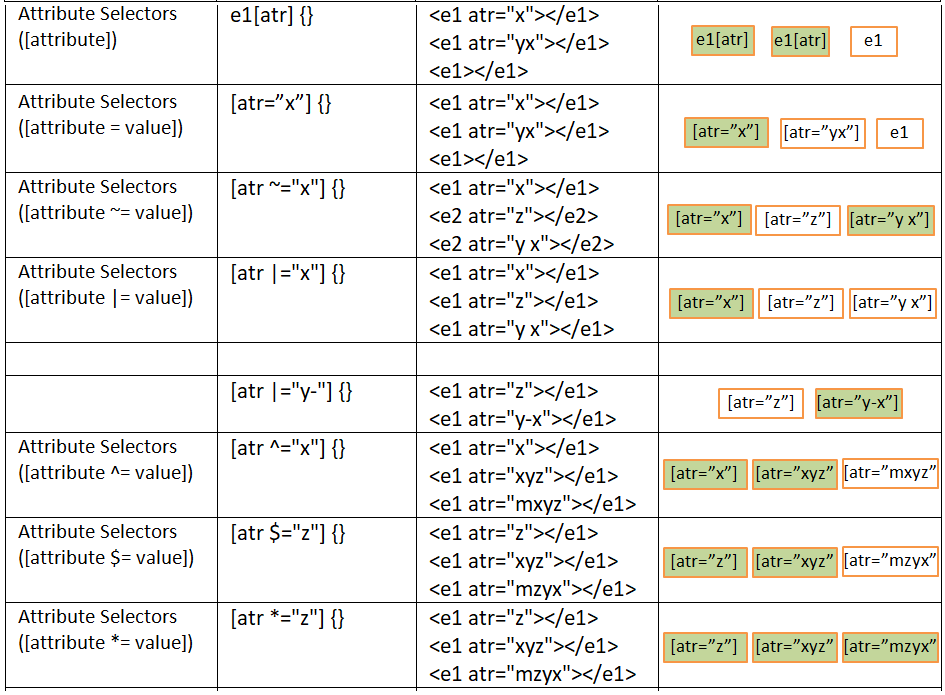
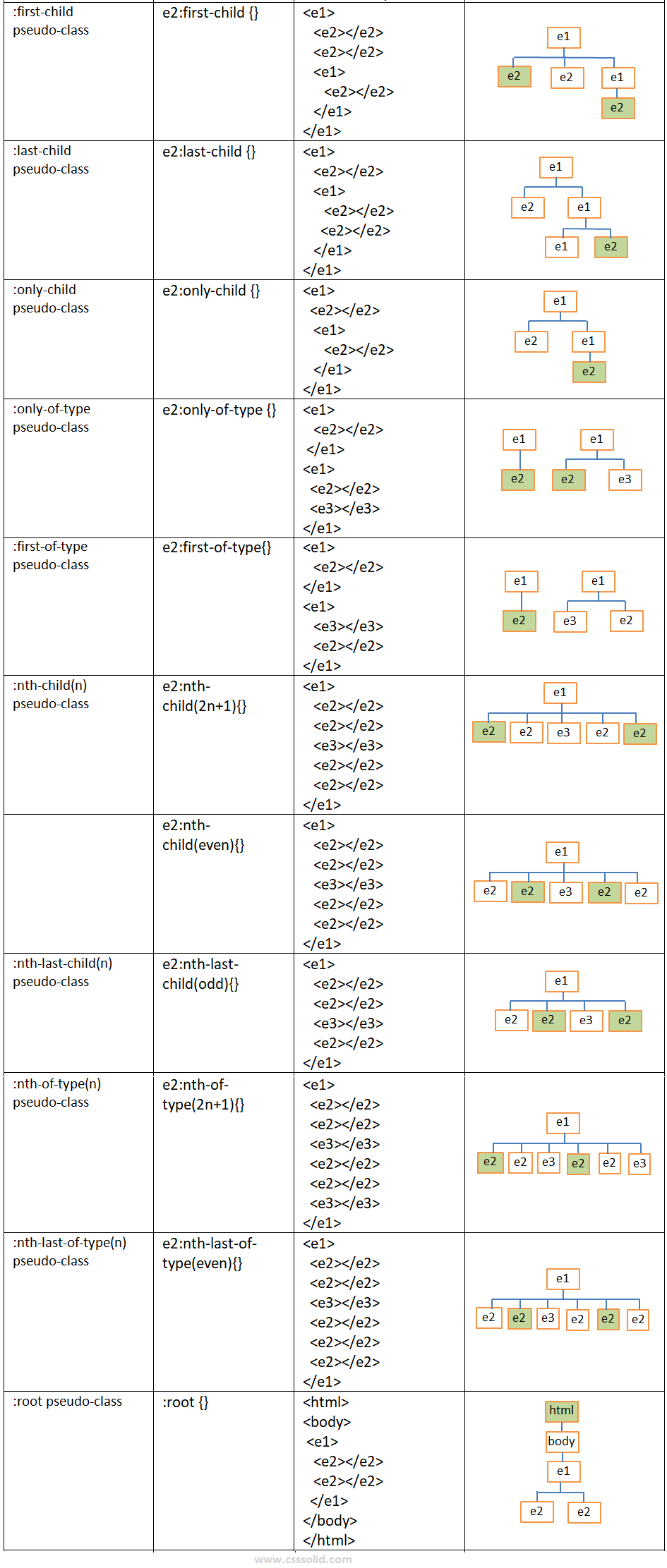
Related selectors are explained using the following links.